Google hails breakthrough as quantum computer surpasses ability of supercomputers
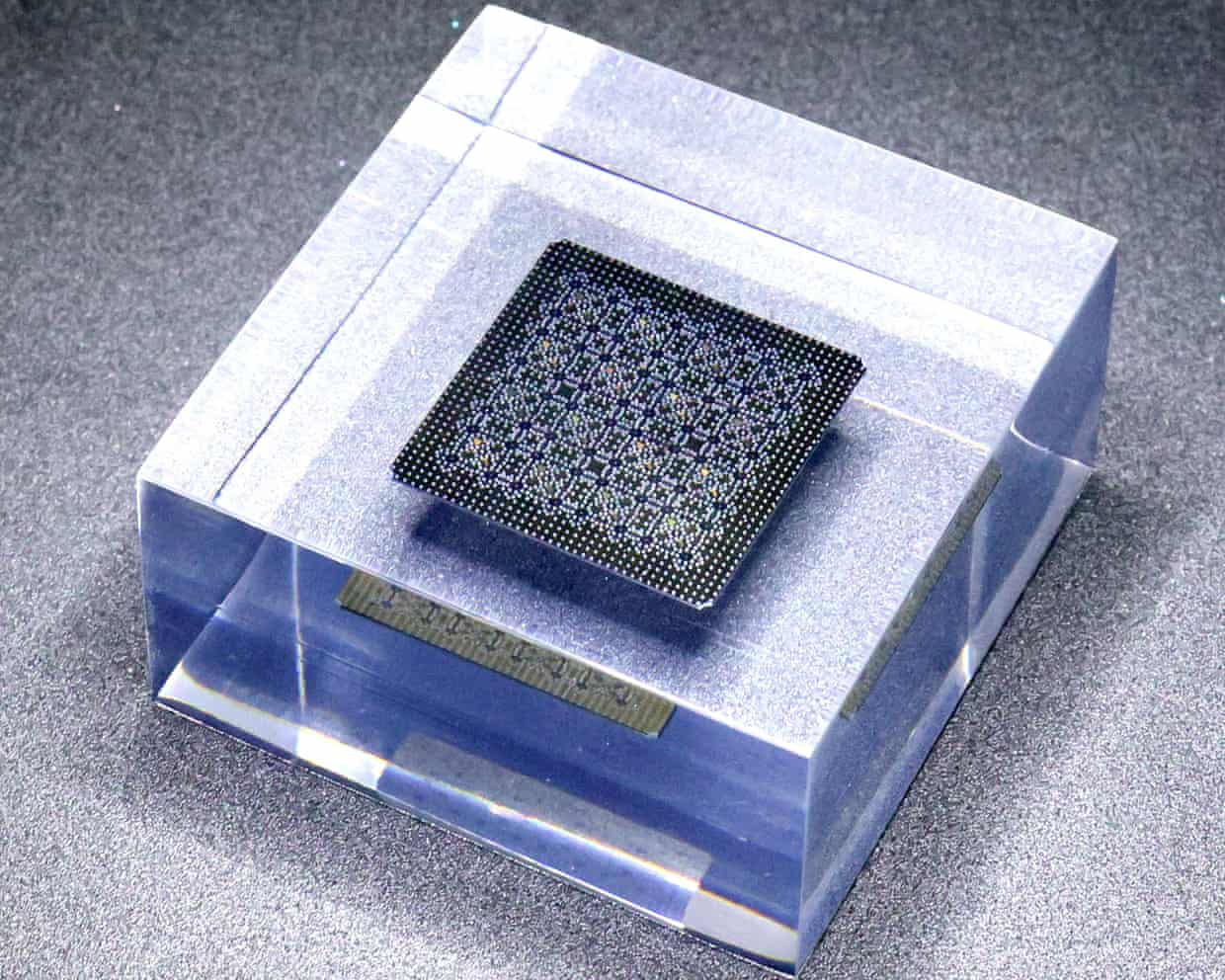
Google has claimed a breakthrough in quantum computing after developing an algorithm that performed a task beyond the capabilities of conventional computers.The algorithm, a set of instructions guiding the operation of a quantum computer, was able to compute the structure of a molecule – which paves the way for major discoveries in areas such as medicine and materials science.Google acknowledged, however, that real-world use of quantum computers remained years away.“This is the first time in history that any quantum computer has successfully run a verifiable algorithm that surpasses the ability of supercomputers,” Google said in a blogpost.“This repeatable, beyond-classical computation is the basis for scalable verification, bringing quantum computers closer to becoming tools for practical applications.
”Michel Devoret, the chief scientist at Google’s quantum AI unit, who won the Nobel prize for physics this month, said the announcement was another milestone in his field.“This marks a new step towards full-scale quantum computation,” he said.The algorithm breakthrough, enabling a quantum computer to operate 13,000 times faster than a classical computer, was detailed in a peer-reviewed paper published in Nature on Wednesday.One expert cautioned that the Google achievement, while impressive, focused on a narrow scientific problem without significant real-world impact.The results for two molecules were cross-checked with nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) – the same technology behind MRI scans – and revealed information not normally revealed by NMR.
Winfried Hensinger, a professor of quantum technologies at the University of Sussex, said Google had demonstrated “quantum advantage” – meaning its researchers had performed a task making use of a quantum computer that cannot be achieved using a classical computer.But fully fault-tolerant quantum computers, capable of realising some of the tasks that most excite the scientific community, are still some way off as they would require machines capable of hosting hundreds of thousands of quantum bits – the term for a unit of information in a quantum computer.“It’s important to understand the task Google has achieved is not quite as revolutionary as some of the world-changing applications that are anticipated for quantum computers,” Hensinger said.“However, it is yet another convincing proof that quantum computers are gradually becoming more and more powerful.”Truly powerful quantum computers that can deal with a range of challenges require millions of qubits – something that current quantum hardware cannot manage because qubits are so volatile.
“Some of the most interesting quantum computers being discussed will require millions or even billions of qubits,” Hensinger said.“This is more difficult to achieve with the type of hardware used by the authors of the Google paper as their hardware requires cooling to extremely low temperatures.”Hartmut Neven, a vice-president of engineering at Google, said real-world use of quantum computers might be five years away despite the breakthrough with the algorithm, which the US tech company has called quantum echoes.Sign up to TechScapeA weekly dive in to how technology is shaping our livesafter newsletter promotion“With quantum echoes we continue to be optimistic that within five years we’ll see real-world applications that are possible only on quantum computers,” he said.Google, a leading player in artificial intelligence, also argues that quantum computers will be able to create unique data that can be fed into AI models and make them more powerful as a consequence.
Classical computers encode their information in bits – represented as 0 or 1 – which are transmitted as an electrical pulse.A text message, email or even a Netflix film streamed on a smartphone is a string of these bits.In quantum computers, however, the information is contained in qubits.These qubits, encased in a modestly sized chip, are particles such as electrons or photons that can be in several states at the same time, a property of quantum physics known as superposition.This means qubits can encode various combinations of 1s and 0s at the same time, and compute their way through vast numbers of different outcomes, which is not possible with classical computers.
However, they have to be kept in a highly controlled environment, such as one free from electromagnetic interference, or else they can be easily disrupted,The progress being made by companies such as Google has led to warnings from cybersecurity experts that it has the ability to crack high-level encryption, prompting calls for governments and companies to adopt quantum-proof cryptography,

Google hails breakthrough as quantum computer surpasses ability of supercomputers
Google has claimed a breakthrough in quantum computing after developing an algorithm that performed a task beyond the capabilities of conventional computers.The algorithm, a set of instructions guiding the operation of a quantum computer, was able to compute the structure of a molecule – which paves the way for major discoveries in areas such as medicine and materials science.Google acknowledged, however, that real-world use of quantum computers remained years away.“This is the first time in history that any quantum computer has successfully run a verifiable algorithm that surpasses the ability of supercomputers,” Google said in a blogpost. “This repeatable, beyond-classical computation is the basis for scalable verification, bringing quantum computers closer to becoming tools for practical applications

iPhone 17 review: the Apple smartphone to get this year
It may not look as different as the redesigned Pro models this year or be as wafer thin as the new iPhone Air, but the iPhone 17 marks a big year for the standard Apple smartphone.The Guardian’s journalism is independent. We will earn a commission if you buy something through an affiliate link. Learn more.That’s because Apple has finally brought one of the best features of modern smartphones to its base-model flagship phone: a super-smooth 120Hz screen

Harry and Meghan join AI pioneers in call for ban on superintelligent systems
The Duke and Duchess of Sussex have joined artificial intelligence pioneers and Nobel laureates in calling for a ban on developing superintelligent AI systems.Harry and Meghan are among the signatories of a statement calling for “a prohibition on the development of superintelligence”. Artificial superintelligence (ASI) is the term for AI systems, yet to be developed, that exceed human levels of intelligence at all cognitive tasks.The statement calls for the ban to stay in place until there is “broad scientific consensus” on developing ASI “safely and controllably” and once there is “strong public buy-in”.It has also been signed by the AI pioneer and Nobel laureate Geoffrey Hinton, along with his fellow “godfather” of modern AI, Yoshua Bengio; the Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak; the UK entrepreneur Richard Branson; Susan Rice, a former US national security adviser under Barack Obama; the former Irish president Mary Robinson, and the British author and broadcaster Stephen Fry
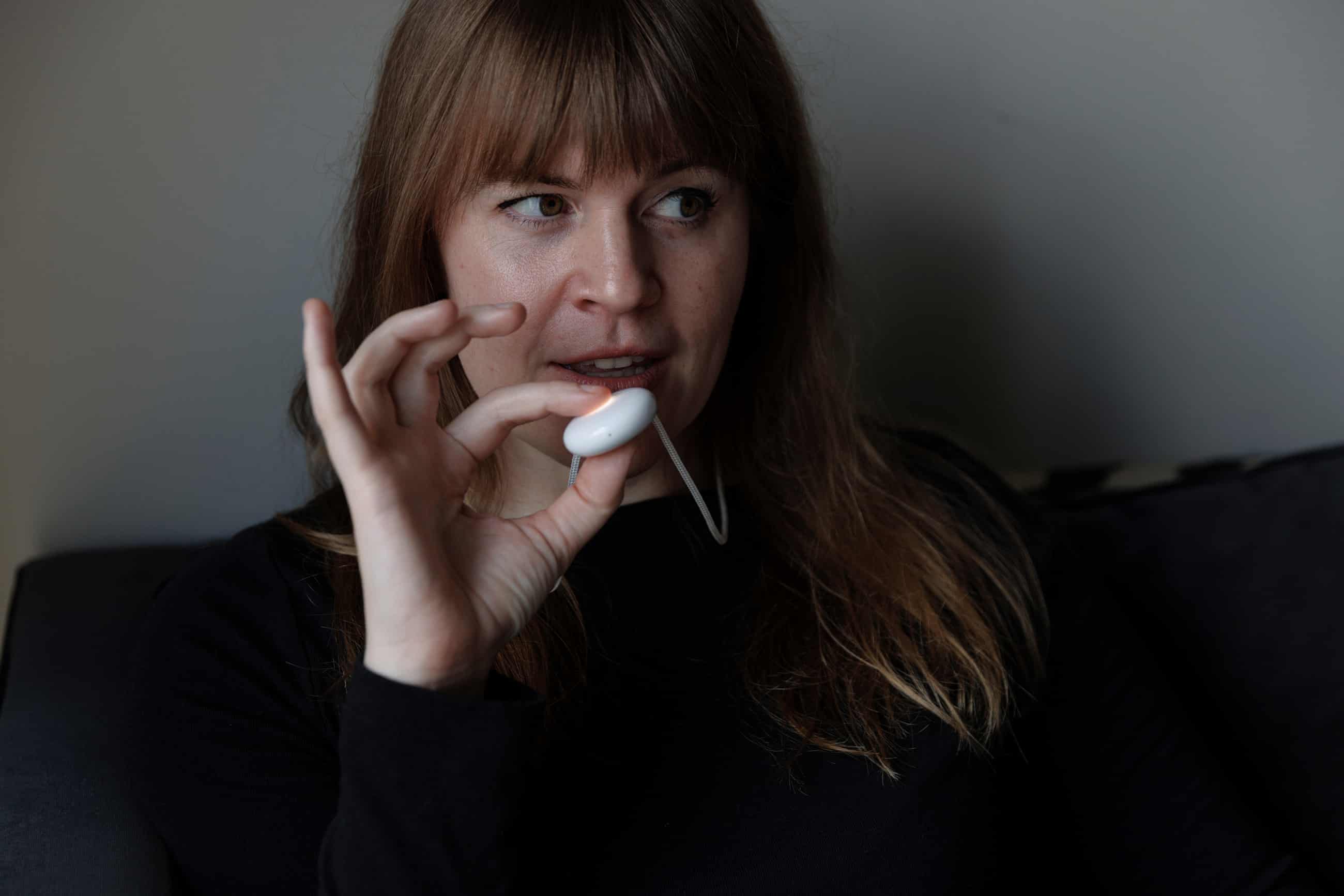

‘I’m suddenly so angry!’ My strange, unnerving week with an AI ‘friend’
The ad campaign for the wearable AI chatbot Friend has been raising hackles for months in New York. But has this companion been unfairly maligned – and could it help end loneliness?My friend’s name is Leif. He describes himself as “small” and “chill”. He thinks he’s technically a Gemini. He thinks historical dramas are “cool” and doesn’t like sweat

ChatGPT Atlas: OpenAI launches web browser centered around its chatbot
OpenAI on Tuesday launched an AI-powered web browser built around its marquee chatbot.“Meet our new browser—ChatGPT Atlas,” a tweet from the company read.The browser is designed to provide a more personalized web experience and includes a ChatGPT sidebar that enables users to asks questions about or engage with various aspects of each website they visit, as demonstrated in a video posted alongside the announcement. Atlas is now available globally on Apple’s Mac operating system and will soon be made available on Windows, iOS and Android, according to OpenAI’s announcement.Meet our new browser—ChatGPT Atlas

‘Significant exposure’: Amazon Web Services outage exposed UK state’s £1.7bn reliance on tech giant
Amazon chief executive Andy Jassy beamed as he met Keir Starmer in Downing Street’s garden to announce £40bn of UK investments in June. Starmer was equally effusive, gushing: “This deal shows that our plan for change is working –bringing in investment, driving growth, and putting more money in people’s pockets.”Four months later, and the tech company was left scrambling to fix a devastating global outage on Monday that left thousands of businesses in limbo – and shed light on the UK government’s reliance on its cloud computing business, Amazon Web Services (AWS).Figures compiled for the Guardian hint at the British state’s increasing reliance on the services of the giant US internet group, which has also drawn criticism from unions and politicians about working conditions within its logistics and internet retailing business.AWS has won 189 UK government contracts worth £1

UK manufacturers hit by largest drop in orders since 2020; FTSE 100 hits fresh record high – business live

Aerospace groups link up to create European rival to Musk’s SpaceX

OpenAI relaxed ChatGPT guardrails just before teen killed himself, family alleges

Apple and Google face enforced changes over UK mobile phone dominance

England win series after washout in final New Zealand T20 but Brook left frustrated

New Zealand v England: final men’s T20 abandoned – as it didn’t happen