AI can help authors beat writer’s block, says Bloomsbury chief

Authors will come to rely on artificial intelligence to help them beat writer’s block, the boss of the book publisher Bloomsbury has said.Nigel Newton, the founder and chief executive of the publisher behind the Harry Potter series, said the technology could support almost all creative arts, although it would not fully replace prominent writers.“I think AI will probably help creativity, because it will enable the 8 billion people on the planet to get started on some creative area where they might have hesitated to take the first step,” he told the PA news agency.“AI gets them going and writes the first paragraph, or first chapter, and gets them back in the zone,” he said.“And it can do similar things with painting and music composition and with almost all of the creative arts.
”Newton, who founded Bloomsbury in 1986 and signed JK Rowling in the 1990s, said there could be a “problem” if AI is used to write entire books.However, he said that readers ultimately look for books written by famous authors.“We are programmed deep in our DNA to be comforted by the authority and the reliability of big brand names, and that applies more than ever to the names of big writers,” he said.“There will be some shoddy content out there so people will turn increasingly to sources of authority for reassurance,” he said.Bloomsbury sales have been increased by a roster of high-profile authors in recent years, including the fantasy author Sarah J Maas, whose popularity has risen on TikTok.
Maas, the author behind the “romantasy” series A Court of Thorns and Roses, has sold more than 70m copies of her books in English across the world.All of the titles have been published by Bloomsbury.Last week the publisher, which is headquartered in London and employs about 1,000 people, experienced a share rise of as much as 10% in a single day after it reported a 20% jump in revenue in its academic and professional division in the first half of its financial year, largely thanks to an AI licensing agreement.Sign up to Business TodayGet set for the working day – we'll point you to all the business news and analysis you need every morningafter newsletter promotionHowever, revenues in its consumer division fell by about 20%, largely due to the absence of a new title from Maas.While Newton argued that AI could help new writers, many prominent authors have clashed with AI companies in recent years.
In September, the AI company Anthropic agreed to pay $1,5bn (£1,1bn) to settle a class action lawsuit in the US by book authors who argued the company took pirated copies of their works to train its chatbot,

Could the internet go offline? Inside the fragile system holding the modern world together
It is the morning after the internet went offline and, as much as you would like to think you would be delighted, you are likely to be wondering what to do.You could buy groceries with a chequebook, if you have one. Call into work with the landline – if yours is still connected. After that, you could drive to the shop, as long as you still know how to navigate without 5G.A glitch at a datacentre in the US state of Virginia this week reminded us that the unlikely is not impossible
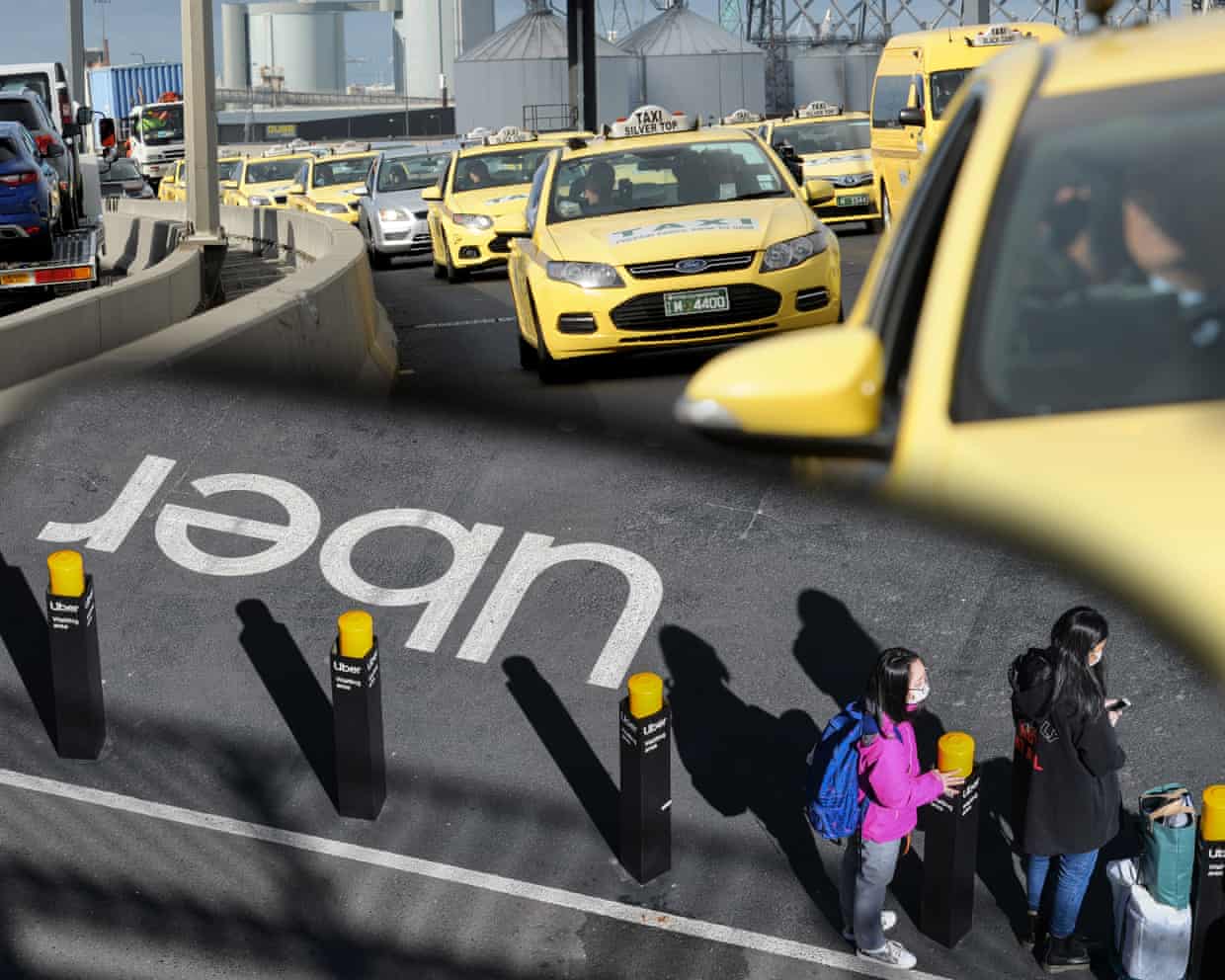

Fare game: what the battle between taxis and Uber means for your airport trip in Sydney and Melbourne
By the time you’ve exited the plane, edged through passport control and endured the baggage claim wait, your only thought may be of home or a hotel bed. But passengers at Australia’s major airports have recently noticed some changes as they contemplate the final leg of their journey.Since Friday, in a bid to deter illegal touts, a new taxi booking trial at Melbourne airport has allowed some passengers to pay a fixed fare upfront. And next month, Sydney airport will begin its own one-year trial of a $60 flat fare for the 13km journey to the CBD.The changes, supported by the taxi industry, are a sign of its struggle to remain competitive with the rideshare companies – especially Uber

Amazon strategised about keeping its datacentres’ full water use secret, leaked document shows
Executives at world’s biggest datacentre owner grappled with disclosing information about water used to help power facilitiesAmazon strategised about keeping the public in the dark over the true extent of its datacentres’ water use, a leaked internal document reveals.The biggest owner of datacentres in the world, Amazon dwarfs competitors Microsoft and Google and is planning a huge increase in capacity as part of a push into artificial intelligence. The Seattle firm operates hundreds of active facilities, with many more in development despite concerns over how much water is being used to cool their vast arrays of circuitry.Amazon defends its approach and has taken steps to manage how efficient its water use is, but it has faced criticism over transparency. Microsoft and Google regularly publish figures for their water consumption, but Amazon has never publicly disclosed how much water its server farms consume
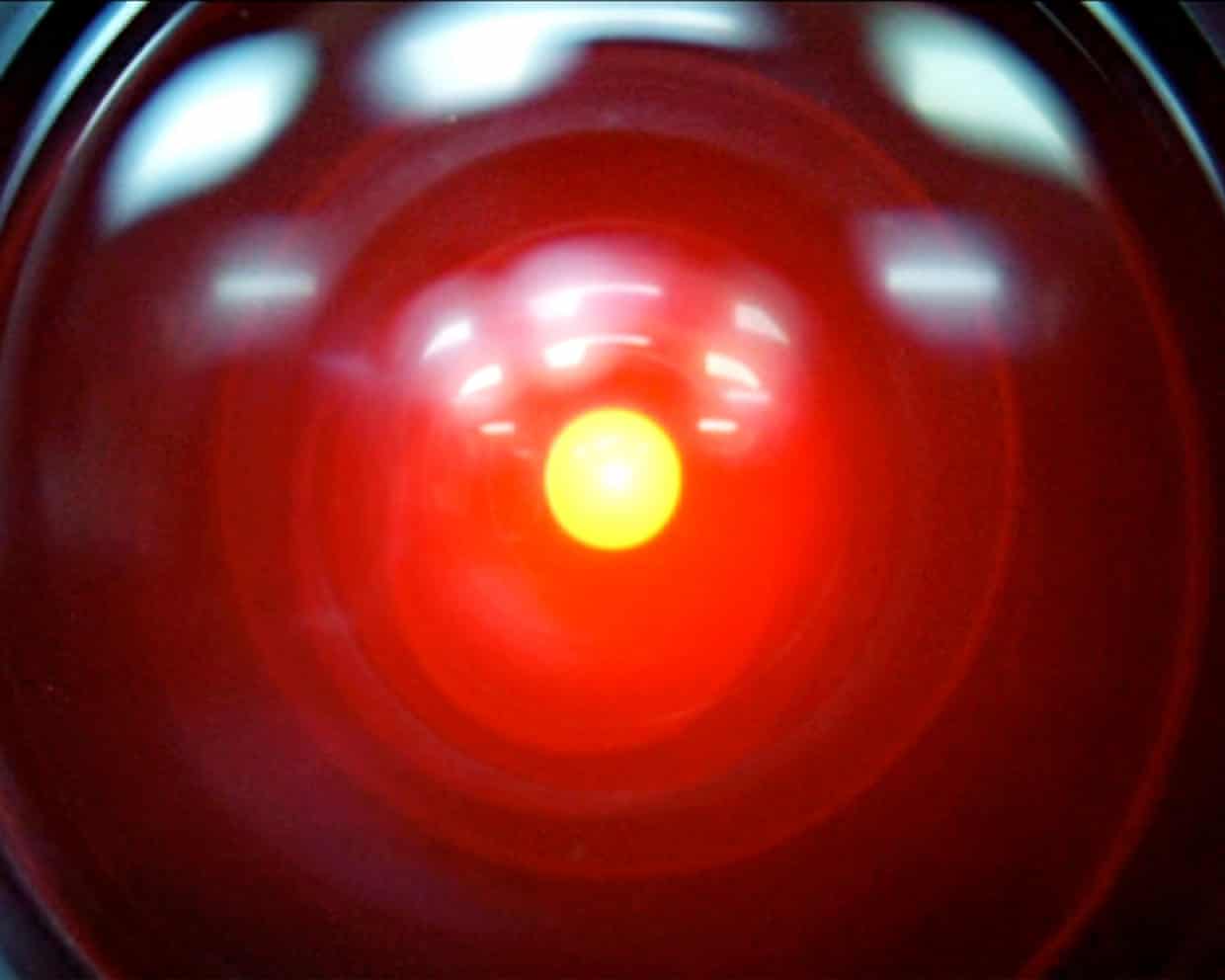
AI models may be developing their own ‘survival drive’, researchers say
When HAL 9000, the artificial intelligence supercomputer in Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey, works out that the astronauts onboard a mission to Jupiter are planning to shut it down, it plots to kill them in an attempt to survive.Now, in a somewhat less deadly case (so far) of life imitating art, an AI safety research company has said that AI models may be developing their own “survival drive”.After Palisade Research released a paper last month which found that certain advanced AI models appear resistant to being turned off, at times even sabotaging shutdown mechanisms, it wrote an update attempting to clarify why this is – and answer critics who argued that its initial work was flawed.In an update this week, Palisade, which is part of a niche ecosystem of companies trying to evaluate the possibility of AI developing dangerous capabilities, described scenarios it ran in which leading AI models – including Google’s Gemini 2.5, xAI’s Grok 4, and OpenAI’s GPT-o3 and GPT-5 – were given a task, but afterwards given explicit instructions to shut themselves down
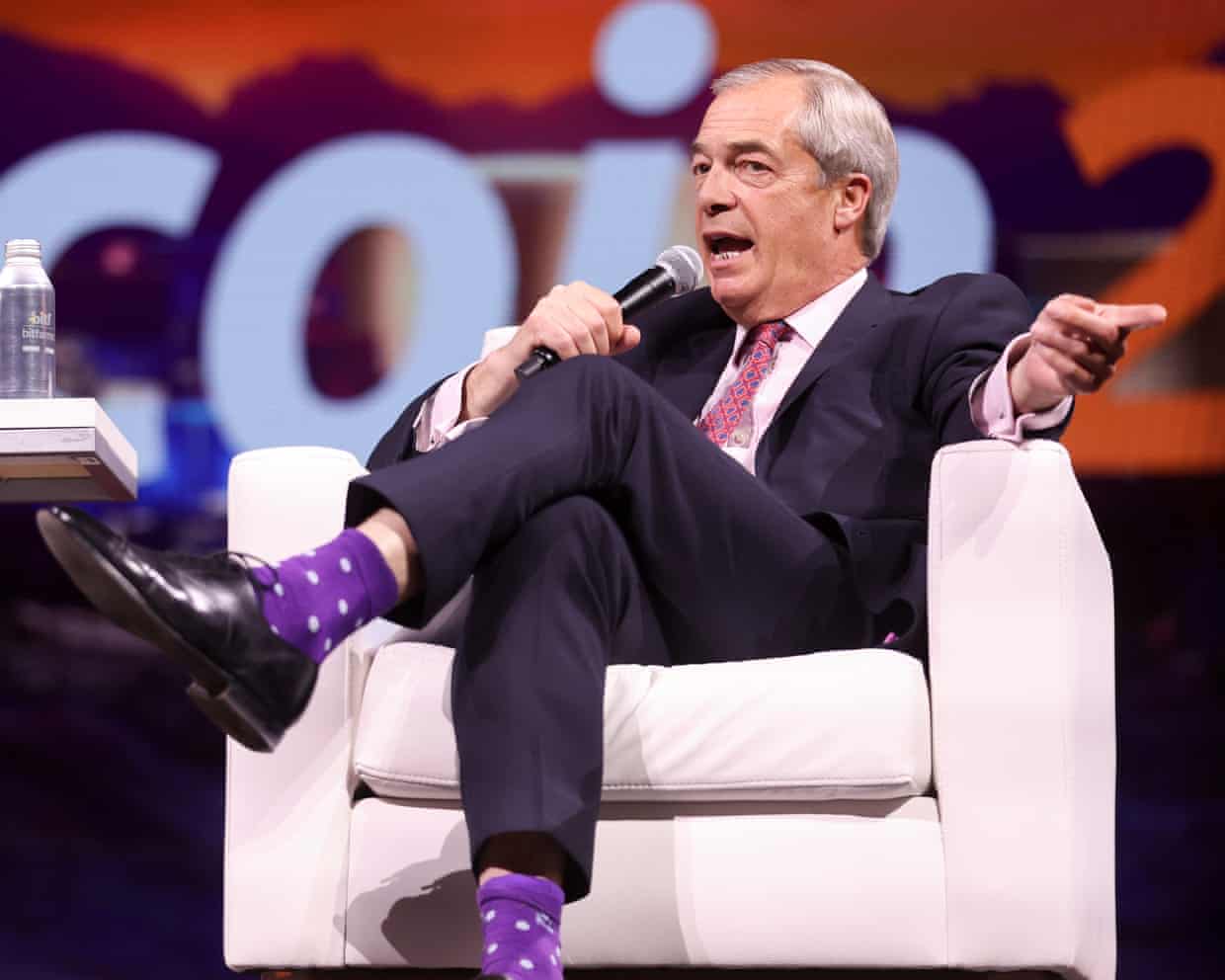

‘He’s one of the few politicians who likes crypto’: my day with the UK tech bros hosting Nigel Farage
It is a grey morning in Shadwell, east London. But inside the old shell of Tobacco Dock, the gloom gives way to pulsating neon lights, flashy cars and cryptocurrency chatter.Evangelists for Web3, a vision for the next era of the internet, have descended on the old trading dock to network for two days. For many, the main event is one man: Nigel Farage.“Whether you like me or don’t like me is irrelevant, I’m actually a champion for this space,” the leader of Reform UK tells the audience of largely male crypto fanatics at the Zebu Live conference

‘Sycophantic’ AI chatbots tell users what they want to hear, study shows
Turning to AI chatbots for personal advice poses “insidious risks”, according to a study showing the technology consistently affirms a user’s actions and opinions even when harmful.Scientists said the findings raised urgent concerns over the power of chatbots to distort people’s self-perceptions and make them less willing to patch things up after a row.With chatbots becoming a major source of advice on relationships and other personal issues, they could “reshape social interactions at scale”, the researchers added, calling on developers to address this risk.Myra Cheng, a computer scientist at Stanford University in California, said “social sycophancy” in AI chatbots was a huge problem: “Our key concern is that if models are always affirming people, then this may distort people’s judgments of themselves, their relationships, and the world around them. It can be hard to even realise that models are subtly, or not-so-subtly, reinforcing their existing beliefs, assumptions, and decisions
‘A medical miracle’: is period blood ‘the most overlooked opportunity’ in women’s health?

England and Wales prison checks to be enhanced after inmate released in error

Social landlords in England now forced to fix emergencies within 24 hours
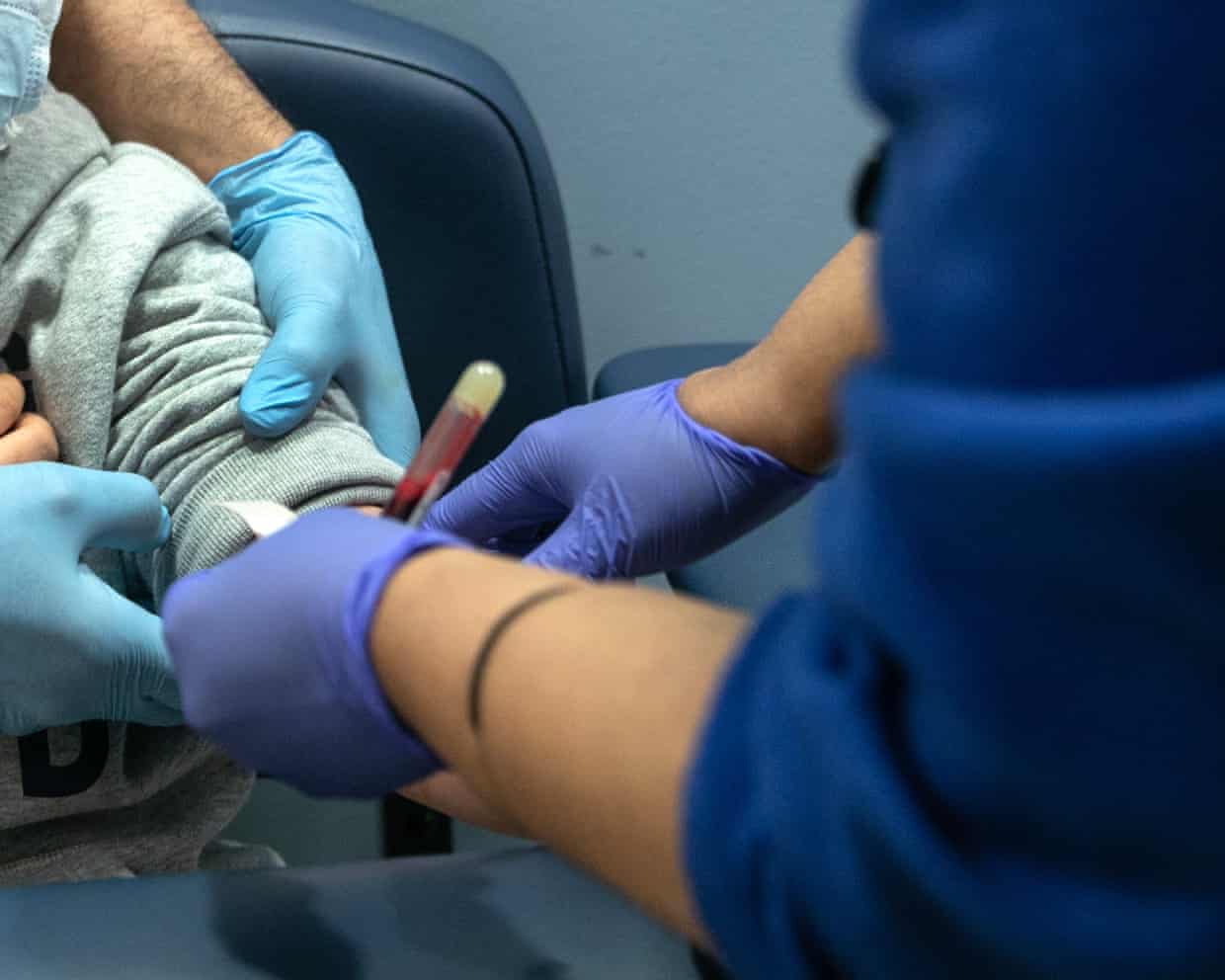
NHS trialling rapid blood test to help diagnose sepsis and meningitis in children

NHS leaders warn of longer waiting times if demand for extra £3bn not met
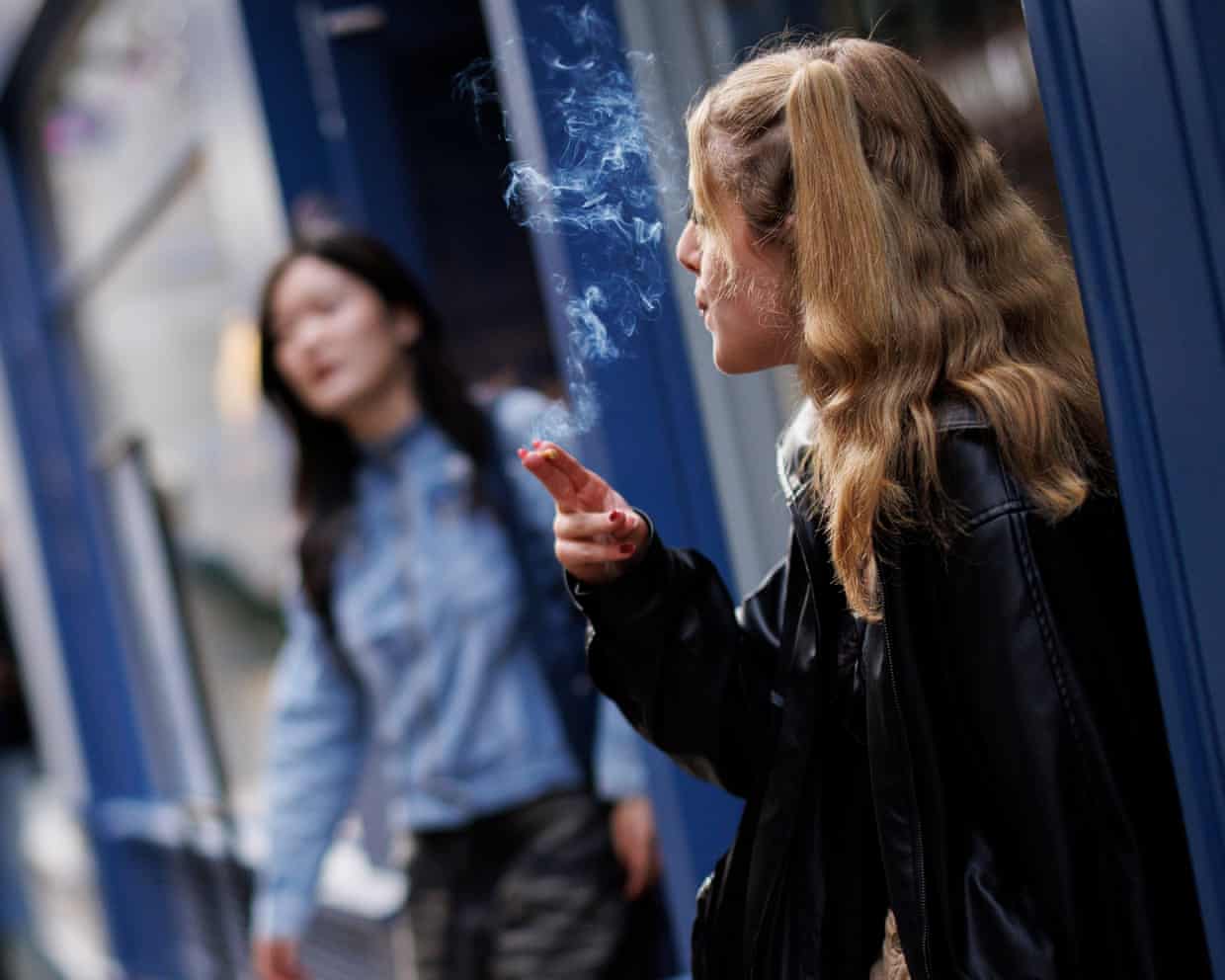

Over 1,200 health leaders call for swift passage of UK tobacco and vapes bill